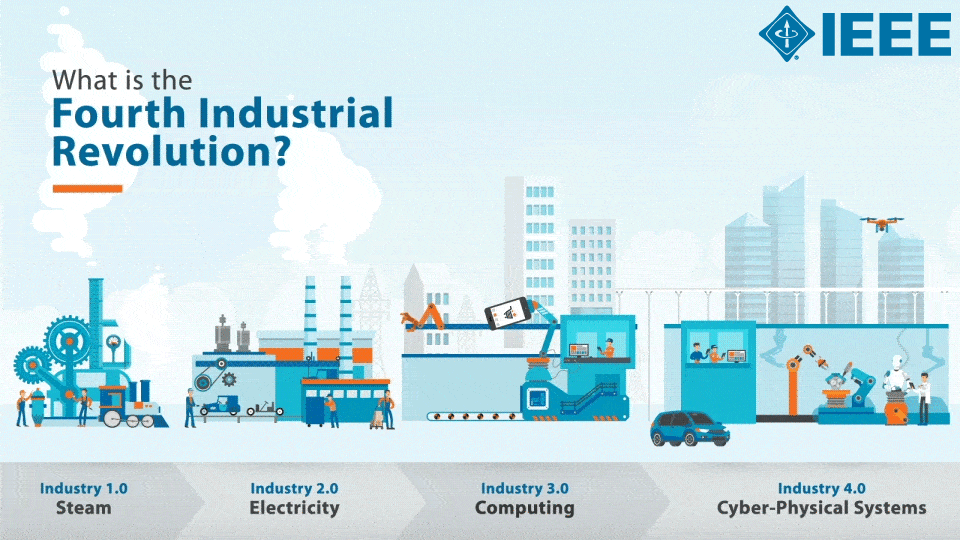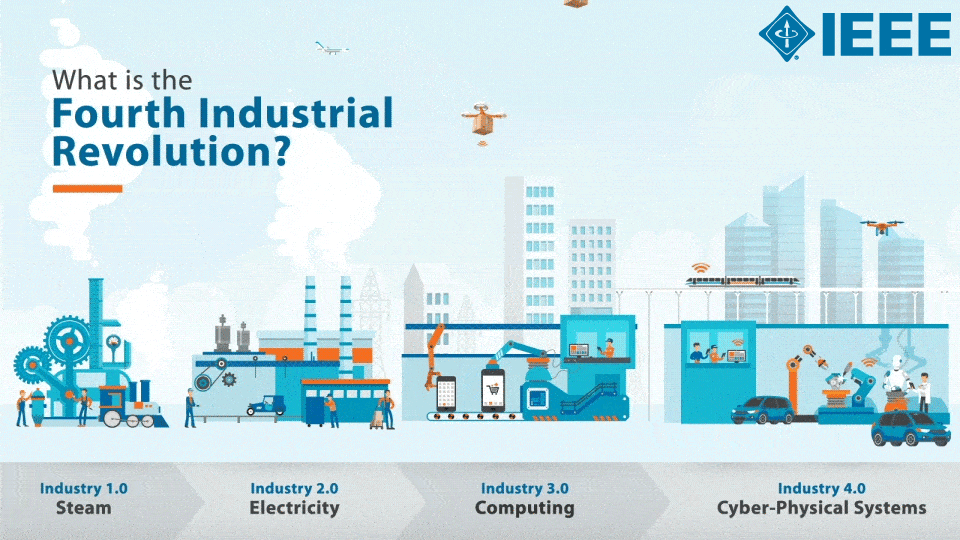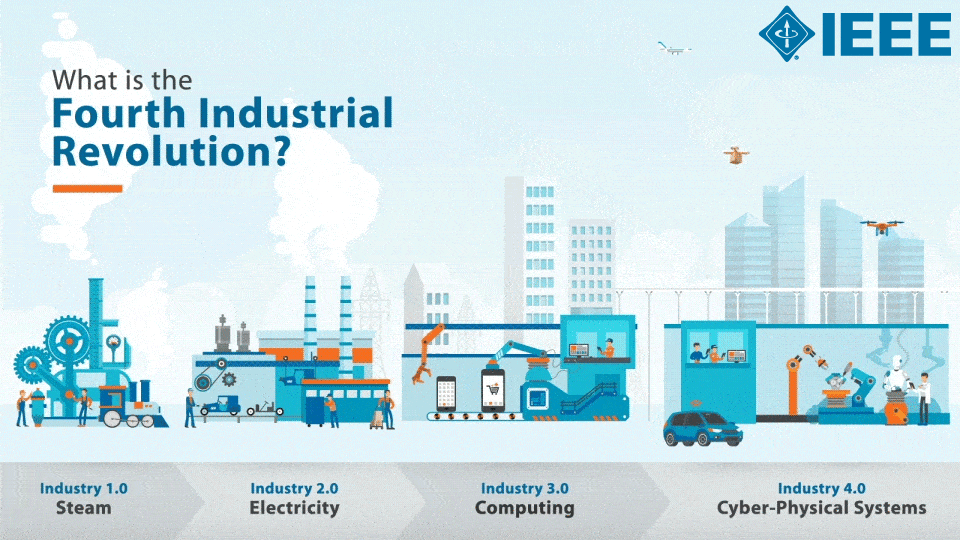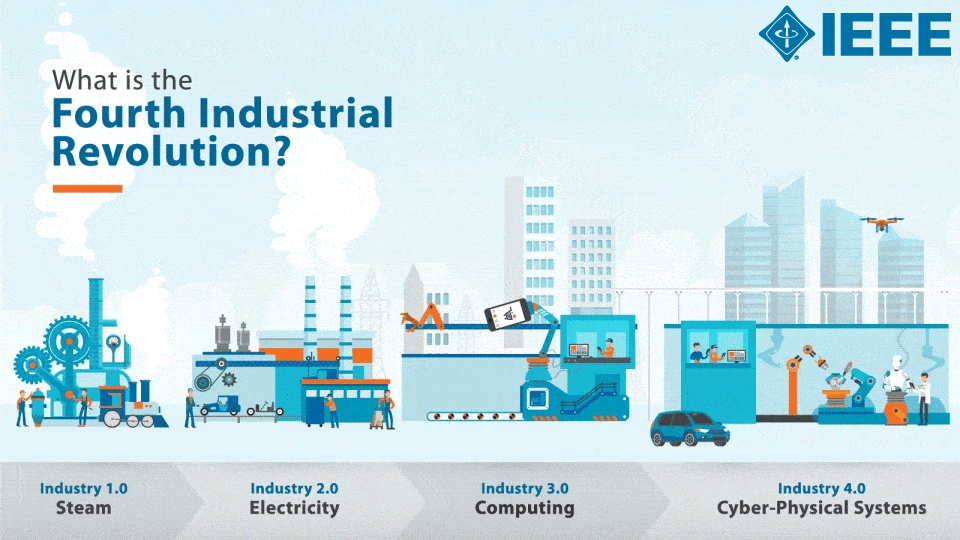
All we need to do to create an accurate and working Machine Learning models is a huge amount of high quality and relevant data. Internet of Things (IoT) devices have the potential to generate a vast amount of data which can be then used with AI. Imagine facial recognition systems using cameras to replace ordinary payments, or recall the current hype for autonomous cars gathering data about surroundings using built-in sensors. Those solutions use both AI and IoT, yet little has been written on how to easily integrate them together. Fortunately, existing IoT platforms provides the interface to gather the data from various devices and can offer a relatively easy way to utilize the IoT data into AI/ML systems. This article will provide you with a few state-of-the-art AI+IoT examples, an overview of the most popular IoT platforms and how they can be integrated with your AI/ML systems.
Just to give you a better feel of how AI can be utilized with IoT, here present two business cases which use both technologies, and a list of some of the most popular IoT platforms with AI capabilities.
ET City Brain
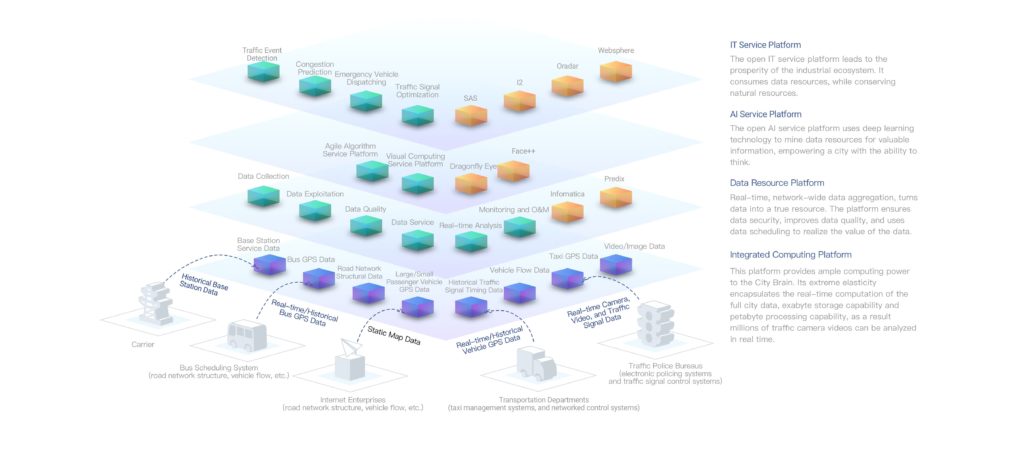
Source : www.alibabacloud.com
ET City Brain, created by Alibaba Cloud, is a complex AI platform solution which optimizes usage of urban public resources. It has been successfully implemented in Hangzhou, China leading to a decrease in car traffics by 15%. The solution also helps to detect road accidents, illegal parking and supports ambulances to reach their target faster by changing the traffic lights to help it reach the patient faster. It is an outstanding software system which utilizes traffic light cameras from the whole city and based on the output of machine learning models it can determine how traffic lights should be changed.
Tesla's Autopilot

Source: Tesla
Tesla autopilot system incorporates GPS, cameras, sonars and forward-looking radars together with specialized hardware to fully utilize the usage of the data coupled into Neural Networks architecture. It works as a self-enclosed system which gathers the data from sensors and then uses a Neural Network model to help determine what should be the next change in the movement of the car .
IoT Platforms with AI capabilities
IoT platforms are getting increasingly popular as they offer a variety of useful tools and cloud storage options for the data streamed from IoT devices. What does each platform offer?
Microsoft Azure IoT Platform
Azure IoT has a Github repository which was created to help you integrate AI and IoT easily. This code repository provides different code examples on how to use Machine Learning and Azure IoT Edge together. Deep Learning models can be packaged in Azure IoT Edge-compatible Docker containers and then exposed to the data using REST APIs. Alternatively, it can be deployed on the cloud and then used for predictions with REST APIs. Azure IoT has a lot of useful tutorials and case examples which are available on their website.
Google Cloud IoT
Google Cloud IoT is an impressive IoT platform which enables you to connect the data to the machine learning model in many different ways. It offers a complete set of tools for edge/on-premises computing with machine learning capabilities, similarly to Azure IoT. Google has also created a separate AI Platform so you can train the model there, together with a cloud storage option for the IoT data. There are few useful tutorials out there: this one, for example, explains how to deploy the ML model to the IoT device which updates itself on the new upcoming data.
AWS IoT
The well-known AWS also offers AI+IoT solutions. AWS IoT Analytics is especially interesting, as it offers data preparation, visualization, and machine learning tools. Machine learning model can be trained using Amazon Sagemaker and then containerized so it can be used with the data stream from IoT devices. ML models can also be uploaded to devices directly where they run much faster and they can also be automatically updated based on the new incoming data.
In conclusion, IoT is making machine connected and communicates with the entire network. IoT also generates Big Data, but AI is only the technology that makes those Big Data useful and meaningful for an industry. A reciprocally beneficial coexistence occurs between IoT and AI technologies. There are tons of domains and business niches, which can reap the advantages of the coexistence of both technologies.
Source: towardsdatascience